- Published on
Binary Trees Intro
- Authors

- Name
- Simon Kurbiel
Introduction
In computer science, a binary tree is a data structure than consists of a root node which can have a left child and a right child. The common approach is for the left child to be then its parent node while the right child is greater than its parent node. Below is an example of a binary tree. 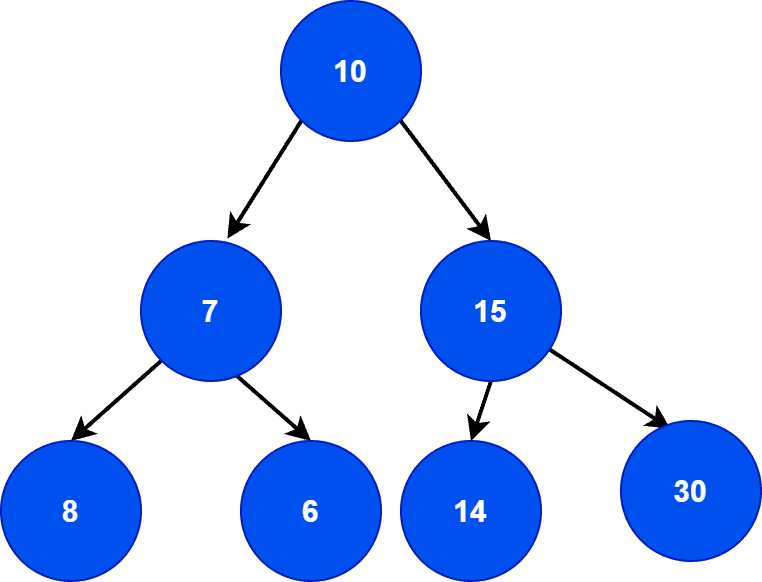
Definitions and Terminologies
Depth or Level Number
- The depth of a node will be it's distance from the root, starting with the root at level 0.
Height of node
- Height of node will be it's distance to the furthest leaf under it, where a leaf (node with no children) node has height 0.
- Let h denote the height of the tree.
Full Binary Tree
A full-binary tree of height h is a binary tree where all nodes at levels have exactly two children, and all leaves are at level . The Example above is a full-binary tree.
It's also very easy to see that the left-child of node will be and its right child will be given that the root node is numbered 1.
The number of nodes in a full-binary tree is
Therefore, the height in a full-binary tree as a function of is:
Complete Binary Tree
- A complete-binary-tree allows for an arbitrary number of nodes n by trimming the nodes of a full-binary-tree at the bottom-level, starting with the rightmost node at the bottom level, and removing as many nodes as needed.
- This is a great article for more info and visuals.
Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self, value:int):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, value:int):
node = Node(value)
if self.root == None:
self.root = node
return
curr = self.root
while(True):
if node.value >= curr.value:
if curr.right == None:
curr.right = node
return
curr = curr.right
else:
if curr.left == None:
curr.left = node
return
curr = curr.left
def inorder(self, root):
if root:
self.inorder(root.left)
print(root.value, end=' ')
self.inorder(root.right)
Running script
if __name__ == "__main__":
import random
bst = BST()
for i in range(10):
bst.insert(random.randint(1,100))
bst.inorder(bst.root)
print("")